Ottolino-Perry K, Tang N, Head R, Ng C, Angarita FC, Acuna SA, DaCosta RS and McCart JA; Int J Cancer. 2014;134(3):717-30
doi.org/10.1002/ijc.28395
Abstract
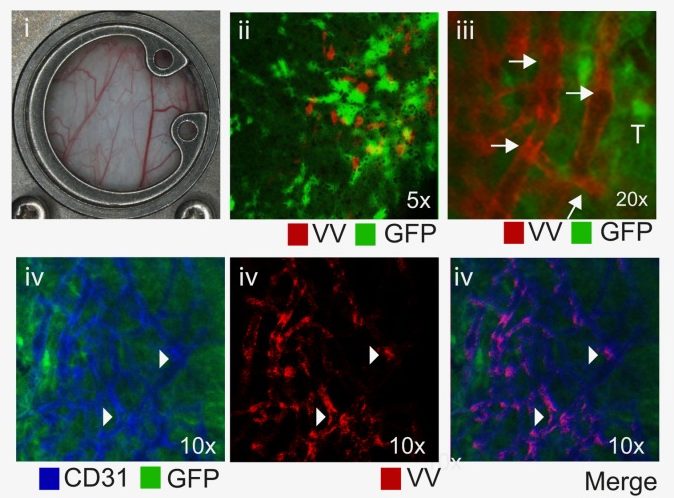
Peritoneal carcinomatosis (PC) represents a significant clinical challenge for which there are few treatment options. Oncolytic viruses are ideal candidates for PC treatment because of their high tumor specificity, excellent safety profile and suitability for peritoneal delivery. Here, we described the use of vvDD-SR-RFP, a recombinant vaccinia virus, in xenograft and syngeneic models of colorectal PC. Colorectal cancer cell lines were highly susceptible to vvDD-SR-RFP replication and cytotoxicity. Intraperitoneal delivery of vvDD-SR-RFP on Day 12 to mice with colorectal carcinomatosis significantly improved survival whereas survival was not improved following virus treatment on Day 8, when tumors were smaller. Immunohistochemistry revealed early tumors had a poorly distributed network of blood vessels and lower proliferation index compared to later tumors. Virus infection was also restricted to tumor rims following Day 8 treatment, whereas it was disseminated in tumors treated on Day 12. Additionally, direct infection of tumor endothelium was observed and virus infection correlated with a loss of endothelial staining and induction of cell death. Our results demonstrate that tumor vasculature has a critical role in virus delivery and tumor response. This will have significant implications in the clinical setting, both in understanding timing of therapies and in designing combination treatment strategies.